Oleg Boev
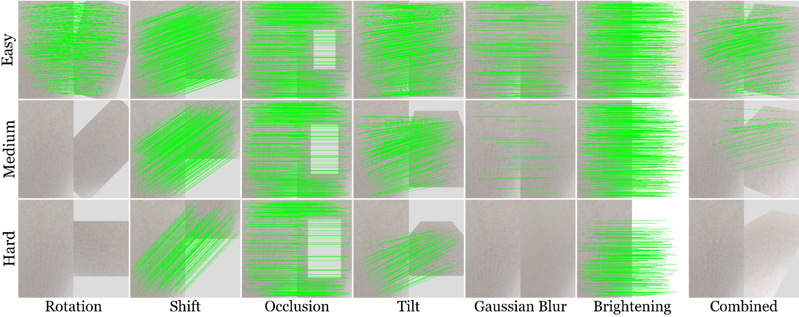
Inlier correspondences on low-texture planar scenes across transformations and difficulty levels.
Overview
LoTex is a failure-oriented empirical analysis of feature matching methods on low-texture planar scenes with weak or repetitive visual structure.
Rather than ranking methods by aggregate scores or leaderboard-style metrics, the study examines how and why matching pipelines degrade under controlled geometric and photometric transformations commonly encountered in real-world acquisition scenarios.
By focusing on systematic failure modes and degradation patterns, LoTex exposes behaviors that are often obscured by standard benchmarks and aggregate performance metrics, with important implications for downstream systems that rely on stable geometric correspondences.
Data and transformations
Dataset
The analysis is based on 250 real images of low-texture planar surfaces, including weakly textured regions, repetitive patterns, and micro-textured materials.

Source images.
Transformations
A controlled set of geometric and photometric transformations is applied at three difficulty levels (Easy, Medium, Hard) to isolate specific degradation factors while preserving known ground-truth geometry. Each source image is paired with synthetically transformed variants using known homographies.
The transformations include rotation, zoom in, zoom out, shift, occlusion, tilt (horizontal perspective), pan (vertical perspective), Gaussian blur, motion blur, darkening, brightening, and a combined transformation designed to approximate realistic camera motion.
In total, the evaluation covers 9,000 image pairs (250 source images × 12 transformation types × 3 difficulty levels).
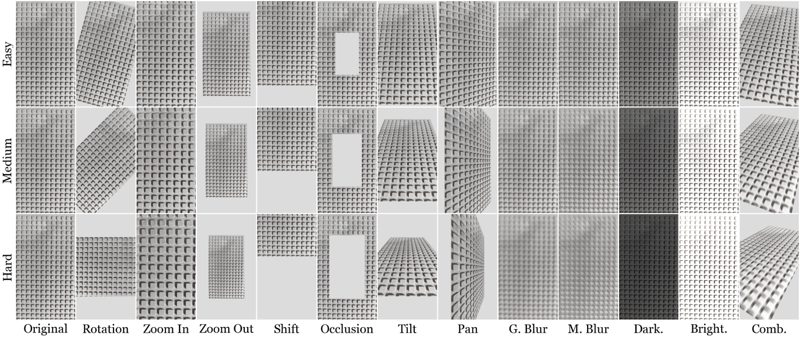
Applied geometric and photometric transformations.
Models
LoTex evaluates 17 representative feature matching methods spanning classical pipelines, learned detector–descriptor systems, dense or global matching approaches, and geometry-aware architectures. While not exhaustive, this set covers a broad range of widely used paradigms and is sufficient to expose systematic failure modes on low-texture planar scenes.
All methods are implemented using a unified backend based on Image Matching WebUI, ensuring consistent feature extraction, matching, and geometric verification across models.
Evaluated methods:
- MASt3R
- DUSt3R
- OmniGlue
- RoMa
- XFeat (Sparse)
- XFeat + LightGlue
- ALIKED + LightGlue
- DKM
- ASpanFormer
- LoFTR
- DISK + LightGlue
- SuperPoint + LightGlue
- SuperPoint + SuperGlue
- D2-Net
- R2D2
- ORB
- SIFT
All models are evaluated using default pretrained weights, without task-specific tuning. Where applicable, a global cap of 2000 keypoints per image is enforced to improve comparability across methods.
Metrics
Evaluation focuses on homography-based robustness and failure behavior. The reported metrics include:
- Homography Reprojection Error (HRE)
- Success Rate at fixed thresholds (SR@τ), defined as the fraction of image pairs whose HRE falls below a given pixel threshold; pipeline failures at any stage contribute a value of zero
- Runtime, measured as the average inference time per image pair
- Auxiliary diagnostics, including inlier statistics and detailed failure metadata
Results
Robustness across transformations
SR@10 is computed over all evaluated image pairs. The results reveal pronounced robustness gaps under rotations, blur, and combined degradations that approximate realistic camera motion.
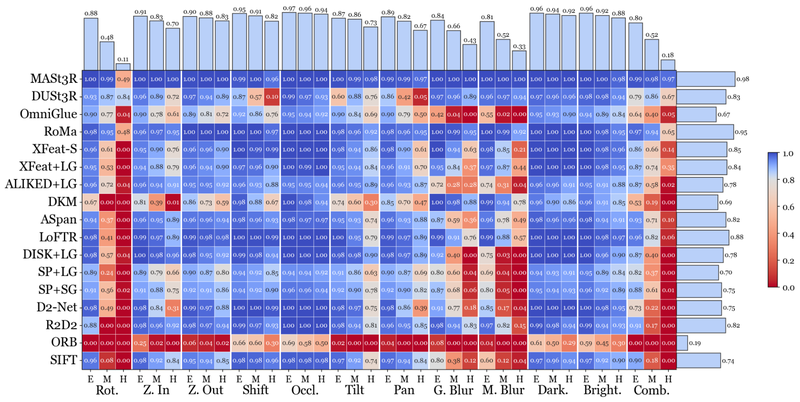
Robustness heatmap (SR@10); the color scale is non-linear, with the neutral color corresponding to SR@10 = 0.8.
Failure and degradation analysis
Homography outcomes are decomposed into accuracy regimes and explicit failure modes, separating gradual geometric degradation from abrupt pipeline breakdowns. Different methods fail in qualitatively different ways, either through smooth degradation with increasing geometric error or through catastrophic pipeline failures. This distinction is particularly important for downstream systems that rely on predictable geometric behavior.
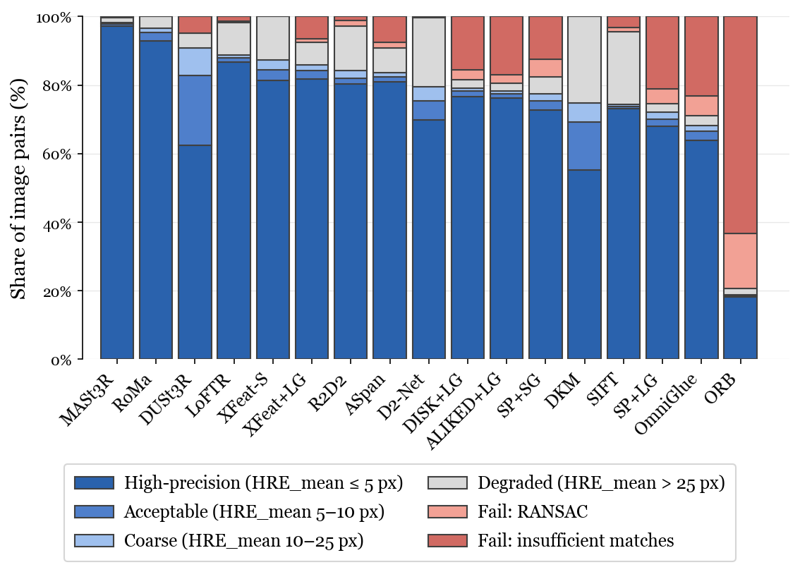
Distribution of geometric accuracy and pipeline failure modes.
Robustness versus efficiency
The trade-off between robustness and computational cost is analyzed by plotting success rate against inference time.
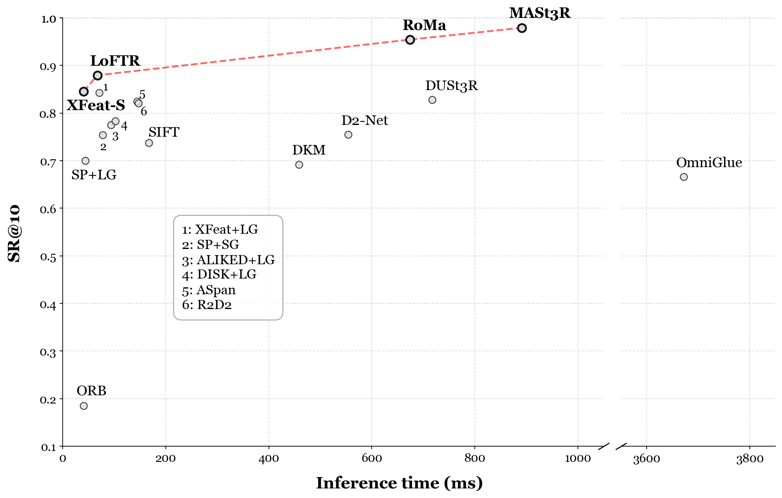
Robustness versus efficiency (Pareto analysis).
Summary
LoTex demonstrates that progress on standard feature matching benchmarks does not necessarily translate to robustness on low-texture planar scenes. The analysis highlights the value of failure-aware evaluation protocols that explicitly expose degradation mechanisms, rather than relying solely on aggregate success metrics.
Citation
@misc{LoTex2026,
author = {Oleg Boev},
title = {LoTex: A Failure-Oriented Analysis of Feature Matching on Low-Texture Planar Surfaces},
year = {2026},
url = {https://smartdatascan.com/research/lotex/}
}